10 Finest Prime Broker Firms For Institutional & Pro Traders In 2025
It has historically been believed that prime brokerages are backed by funding banks, which are some of the strongest financial organizations in the world. Nonetheless, the collapse of Lehman Brothers and different such funding banks has exposed a flaw in the prime brokerage mannequin. It is not unusual for both hedge funds and investment banks to hedge their bets so that their interests are shielded from credit score risks in the occasion of the failure of both of the counterparties.
This could be an important issue in the decision, particularly for a new fund that’s just beginning up and actively in search of main buyers. Understanding prime brokerage highlights how main market players navigate and optimize their operations. This overview explores numerous Cryptocurrency wallet aspects of prime brokerage, emphasizing its relevance and evolving trends inside the trade. Investingintheweb.com doesn’t present any supply or solicitation to buy or sell any funding products, nor does it represent an offer to offer funding advisory companies.
This flexibility permits hedge funds to pursue distinctive funding goals. Additionally, prime brokers present entry to a broad range of markets and asset courses, enabling hedge funds to diversify portfolios and capitalize on global alternatives. A “Prime” Forex dealer, in the context of foreign exchange (Forex) buying and selling, refers to a brokerage agency that has direct entry to the interbank market.
Shoppers prefer searching by way of the crypto and synthetic prime brokerage list as a outcome of ability of such accounts to customize and intensive market entry. They lend securities, fund hedge funds, commerce with leverage, and hold custody of property globally. Primer brokerages supply services outdoors that of executing brokers at a cost. For formidable traders that may scale their strategies and seek to function a hedge, a main dealer shall be wanted in time. Prime brokers facilitate the handling of enormous securities transactions and will present the necessary instruments to enhance your trading operations if your small business is worthy sufficient for the prime dealer.
For example, a prime broker may also be in the enterprise of leasing office house to hedge funds, as well as including on-site services as part of the arrangement. Threat management and consulting companies could also be amongst these, particularly if the hedge fund has just started operations. Prime brokerage is a premium bundle that some financial establishments provide their greatest and most energetic trading purchasers such as hedge funds and money managers. They serve clients corresponding to smaller banks, retail brokers and hedge funds, who can’t meet the requirements to make use of the companies of a Prime broker. A “Prime of Prime” (PoP) Forex broker, however, serves a slightly totally different position in Forex. These are companies that provide brokerage services to these shoppers who may not be massive enough to immediately entry prime brokerage providers.
What Is Margin In Prime Brokerage?
Buyers ought to assess the firm’s degree of consumer assist and ensure that it meets their expectations. Financial Institution of America Merrill Lynch’s sophisticated expertise platforms and devoted consumer service groups be positive that https://www.xcritical.com/ purchasers receive the best level of assist and steerage. Their dedication to innovation and excellence makes them a leading alternative for institutional buyers.
Subsequently, environment friendly money management is important to the company and its soundness. Furthermore, a crypto prime brokerage account assists institutional buyers and hedge funds via larger availability of liquidity and belongings. The prime brokerage enterprise, both conventional and crypto funding, attracts a number of funding banks since it’s a vital revenue supply and guarantees assured results. Moreover, it has evolved from the continuous increment of hedge fund operations.
Navigating Financial Transactions
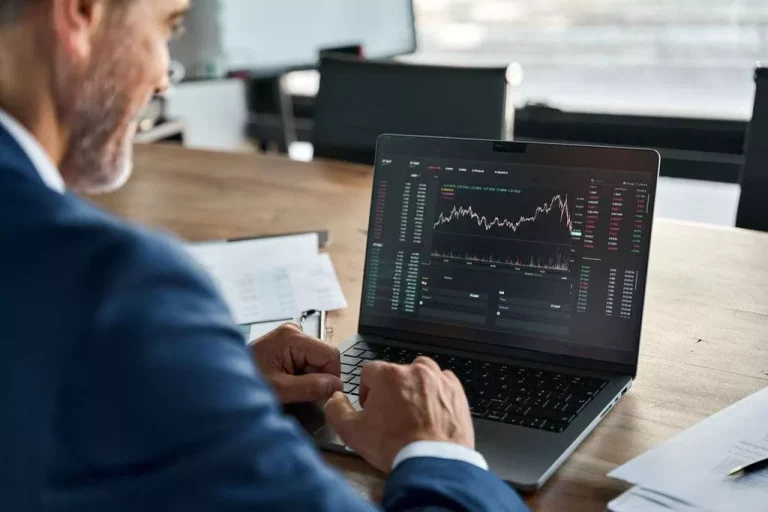

Please observe that it includes facilitating the clearing accounts and settlements for hedge funds and different purchasers. Clearing denotes confirming the transaction settlement with a timely switch of shares and funds to both sides. After six months, ABC has grown and its funding strategy has become extra advanced. It must borrow securities as part of its funding technique and transacts with J.P.
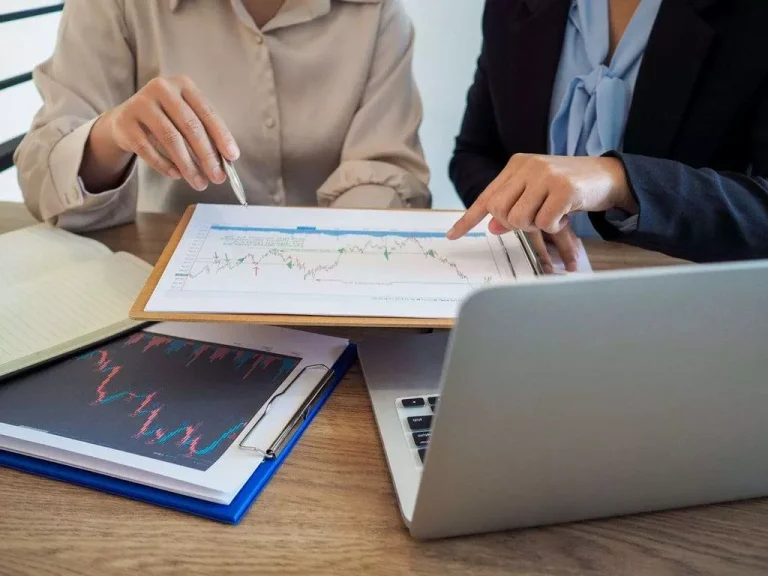

This partnership helps funds deal with monetary markets with more confidence and efficiency. Quick sale locates, access to dark pools and clearing are all a part of the core business of prime brokers. Leverage is considered one of the major benefits of utilizing a major broker since they have custody of its purchasers belongings, the prime broker is capable of utilizing those belongings to lever extra shopping for power to its shoppers. The perfect prime brokerage consumer will make beneficiant use of its obtainable leverage whereas having plenty of margin available so as not to trigger any margin calls, force liquidation or defaults. Most prime brokers search to service hedge funds, establishments like pension funds, and business banks.
Maintain in thoughts that a prime brokerage makes its cash from fees, interest on loans (cash, margin, and securities), and commissions. Primarily Based on this, the larger your property under administration (AUM), transactions, and compelling your methods are the more attractive you are as a consumer. It can vary from as little as $500,000 to $40 million to $50 million in assets. Prime brokers additionally provide entry to their shopper pool for capital introduction to increase the online asset value of hedge funds.
In addition, the brokers could rework toxic belongings from the steadiness sheet into securities through securitization, which can now be traded. To clarify, custodians are monetary establishments holding their clients’ securities like bonds and choices for defense. It generally holds high-value securities in both digital and physical types. This includes all kinds of accessible securities in the monetary business. Precisely, safety lent to the mortgagor implicates the transferral of ownership and title. Accordingly, the broker expenses a mortgage charge, including the borrowing rates and any curiosity specified by the contract.
- This implies that they are successfully an intermediary in all of the transactions of the consumer.
- These providers typically embody commerce execution, securities lending, and risk management.
- Retail traders usually interact with retail Forex brokers, who may in turn be shoppers of Prime of Prime brokers.
- Skilled merchants and institutional traders typically use Prime Forex brokers, as they offer extra advanced and complex trading options.
- They cater to beginners and professional traders by providing free instructional assets by way of their IG Academy and professional insights through their information and evaluation section.
Like Prime brokers, PoPs additionally earn via commissions on trades and markups on spreads. They similarly profit from offering access to leverage and margin buying and selling, charging curiosity or charges on these companies. World custody providers imply prime brokers work with custodian banks to maintain property protected.

What Are The Biggest Prime Brokerages?
Since they’re more lively with buying and selling and tend to generate extra commissions and costs, prime brokers also prefer these active individuals. Prime brokers have a critical half in offering introduction to new capital for hedge funds. Hedge funds also profit from the core service offerings on up to the more concierge type further providers which may be supplied to the bigger purchasers.
For traders, securities lending can improve portfolio returns by way of lending fees, while borrowers gain the ability to implement numerous buying and selling strategies. Notably, famous investment banks, together with JPMorgan Chase & Co, Morgan Stanley, and Goldman Sachs Group Inc, are the most vital market players in this business. Moreover, conventional and crypto prime brokerage providers embrace money administration, securities lending, custodian providers, and settlement companies. Prime brokerages, at times referred to as prime brokers, are generally bigger financial establishments which have dealings with different major institutions and hedge funds. The majority of large banks have prime brokerage units that service hundreds of purchasers. Though prime brokerages offer all kinds of providers, a consumer isn’t required to take part in all of them and also can have providers carried out by other establishments as they see fit.
This might embody over the counter derivatives, and exchange-traded derivatives, or a combination of the two. This is the explanation why these prime brokers are capable of present more liquidity to their purchasers. IG provides web-based and cell trading platforms that enable customers to commerce throughout forty global financial markets, with a processing capacity of 15 million trades per thirty days. L2 Dealer, IG’s proprietary platform, offers Direct Market Entry (DMA) execution utilizing native, synthetic, and algorithmic order types, supported by Tier 1 financial institution sensible order routing (SOR) technology. IG’s trading platform is designed to provide quick, best-in-class execution, with the power to handle giant volumes of trades rapidly.